
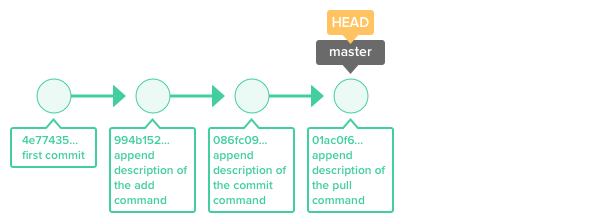
then using the following commands git checkout commit ID - path/to/file git commit -m 'commit message' will help you to revert the file you want to latest version of that file on remote computer. This command deletes the branch we are in. you need to find the latest commit id and the directory of the file you want to revert. Before running the following command, we need to make sure we're on the main branch. But there is another way to do this with a single command. Now we have the latest changes, and we are in a brand new main branch. In Git, there are two ways to refer to a particular commit, one of being absolute and the other relative. The first step being, identify the version you’re in so you can start searching for the version you want to revert to. It is a default option in git revert command.
git revert(We can keep it to preserve history if we want to.) git branch -D old_main We can actually move the HEAD reference to point at anything we want, though, and this is the key to rolling back versions. To revert a commit, we need the commit reference id. The last thing is deleting the old_main since we don't need it anymore. But it still has all the files from the old_main, because we created a new branch while we were in the old_main branch. The new branch is totally disconnected from all other branches and commits. orphan creates a new branch without a root so that the newly created branch doesn't have a history and a parent. Next, we need to create an orphan branch from the current head.

Now our branch looks like this: old_main:main.
This moves everything (all the commits and history) from the main branch to the old_main branch. Git Revert revert is the command we use when we want to take a previous commit and add it as a new commit, keeping the log intact. m or -move is used to rename/move the branch and its reflog. We will lose all the branches and the commits.įirst, we need to rename the main branch (Before running this command, we assume a branch named old_main doesn't exist.). This command deletes everything related to Git in the repository. Instead, we either have to change our main (using -orphan) or delete the branch while we're on it.ĭon't use rm -rf. Both of them have security mechanisms to prevent this action. When we want to change the initial commit on the main (or master) branch, we cannot use interactive rebasing and resetting.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
